format() method
This method will provide you with the formatted string that is specified by the given arguments or the format. In case you o not provide the locale in String.format() method it will use the default locale using the Locale.getDefault() method. This method will work exactly like the sprintf() function in the C language.
Method implementation-
public static String format(String format, Object... args) {
return new Formatter().format(format, args).toString();
}
Syntax-
public static String format(String format, Object... args)
and,
public static String format(Locale locale, String format, Object... args)
This method may throw two types of error- NullPointerException and IllegalFormatException.
Example-
public class Simple{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String s1="java";
String s2=String.format("%s",s1);
String s3=String.format("%f",65.869);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
}
}
Output-
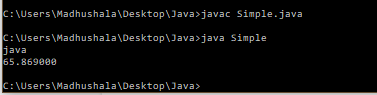
Below is the list of the format specifiers-
|
Format specifier |
Data type |
Description |
|
%a |
floating-point (except BigDecimal) |
Iit will return the Hex output of the floating-point number. |
|
%b |
Any type |
"true" if non-null, "false" if null |
|
%c |
character |
It will represent the Unicode character |
|
%d |
integer (incl. byte, short, int, long, bigint) |
It will represent the Decimal Integer |
|
%e |
floating point |
A decimal number in scientific notation |
|
%f |
floating point |
It will represent the decimal number |
|
%g |
floating point |
A decimal number, possibly in scientific notation depending on the precision and value. |
|
%h |
any type |
Hex String of value from hashCode() method. |
|
%n |
none |
Platform-specific line separator. |
|
%o |
integer (incl. byte, short, int, long, bigint) |
It will represent the Octal number |
|
%s |
any type |
It will represent the String value |
|
%t |
Date/Time (incl. long, Calendar, Date and TemporalAccessor) |
%t is the prefix for Date/Time conversions. |
|
%x |
integer (incl. byte, short, int, long, bigint) |
It will represent the Hex string. |
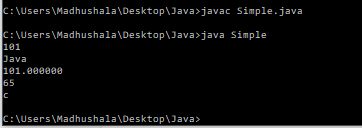
Example-
public class Simple{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = String.format("%d", 101);
String s2 = String.format("%s", "Java");
String s3 = String.format("%f", 101.00);
String s4 = String.format("%x", 101);
String s5 = String.format("%c", 'c');
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
System.out.println(s4);
System.out.println(s5);
}
}
Output-